How to be a BA from a PMO analyst role in 2025
As a career option, the business analyst role offers greater challenges and higher compensation. As we find in the salary comparison below, the average annual salary for PMO Analysts is 54K, whereas, for Business Analysts, it is 75K, a whopping 40% higher. The good news is that one can move into a Business Analyst role from a PMO analyst role as they have many common skills.
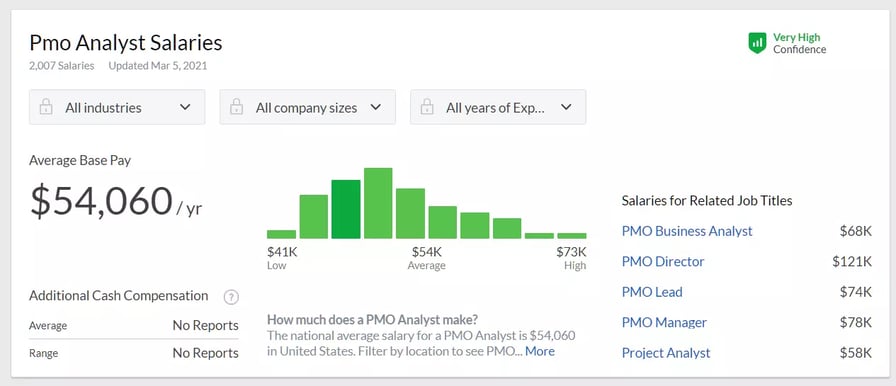
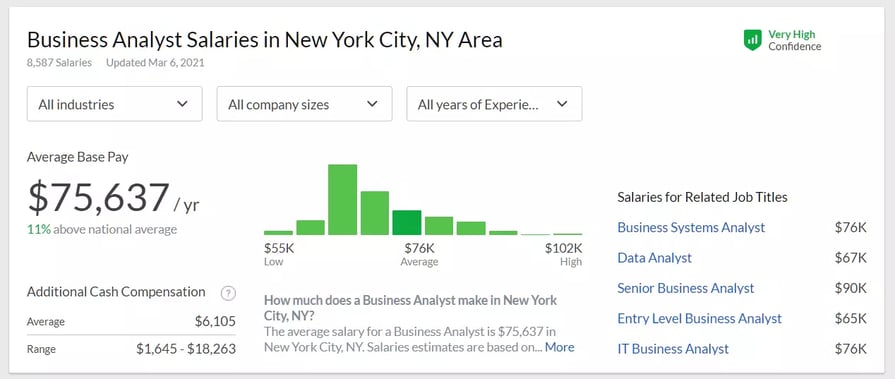 Image Source: Glassdoor
Image Source: Glassdoor
Let's do a deep dive on these two roles and find how one can become a business analyst from a PMO analyst.
What is a PMO Analyst?
A PMO Analyst works in a Project / Program Management Office (PMO). PMO is the command center for delivery organizations, portfolios of projects, programs, and large projects. PMO Analysts track the information that comes into this command center and make sure everything runs smoothly. PMO analysts ensure projects stay on track, within budget, and work is performed efficiently and effectively. PMO Analysts work with employees at all levels who are project stakeholders.
PMO Analyst Duties and Responsibilities
To manage and track the progress of projects, PMO Analysts perform many tasks in their day-to-day work. Some of the primary PMO Analyst duties and responsibilities are mentioned below:
Monitor Projects
PMO Analysts monitor existing programs and projects to ensure that they are executed & completed on time. Their job is to keep track of project development and track that each stage is completed within the boundaries of time and budget but still adheres to the right quality.
Analyzing Data
One of the key responsibilities of a PMO Analyst is analyzing and reporting project information to senior management to guide their decision-making.
Prepare Project Status Reports
Along with the Project Manager, PMO Analysts work to develop status reports to be delivered to the Delivery head and senior management. They report variances in the project timeline or cost.
Oversee Employee Manpower
Often, PMO Analysts are responsible for predicting manpower requirements and providing the same to the HR function.
PMO Analyst Skills
PMO analysts are talented multitaskers. They are well organized. They excel at understanding the "big-picture" and yet having a keen eye for detail. They are strong communicators, able to communicate with the staff they interact with and with senior management.
Core skills
-
Knowledge of project management tools and techniques.
-
Excellent computer skills.
-
Experience with program coordination/administration.
-
Strong skill in reporting.
Advanced skills
-
Knowledge of forecasting
-
Certification in Project Management
What is a Business Analyst?
A Business Analyst is a professional who works in a change initiative. Business Analysts identify, validate, elicit, and verify business needs. Business analysts ensure stakeholders have a common understanding of the change, and they collaborate for successful change. Business Analysts work with employees at all levels who are project stakeholders.
Business Analyst Duties and Responsibilities
Assess Business Needs
Key duties of the business analysts are assessing a business' future technology needs, mainly by meeting directly with stakeholders. Business analysts assess an organization's current technologies and capacities to determine where they can be enhanced to help the business run more effectively or if a new system needs to be developed or procured.
Determine Project Scope and Requirements
While making decisions regarding enhancements, business analysts also play an important role in determining each project's scope and requirements. Business analysts liaise with both the stakeholders to prepare project specifications and ensure that they align with the overall project goals.
Communicate Between Business and Development Teams
Throughout the enhancement process, Business analysts support communication between Development team members and stakeholders. In many cases, business analysts foster communications between teams.
Participate in System Testing
Many Business analysts also take an active role in system testing. They participate in system testing to ensure that the system meets requirements, can be used before and after deployment, and gather user data to make recommendations for improving functionality or reliability.
Provide Procurement Advice
In many organizations, Business analysts provide direct advice to stakeholders and executives on system procurement. They identify software products that could easily resolve a business-critical need and make recommendations to decision-makers, providing information about costs and benefits aiding business decisions.
Assist Implementation
Business analysts work directly with development teams during the implementation and deployment processes. They provide guidance based on their own experiences as well as information gathered from users.
Business Analyst Skills and Qualifications
Business analysts act as a bridge between business leaders and technical teams. Companies tend to hire candidates with at least a bachelor's degree and the following skills:
Requirements elicitation – Business analysts elicit information related to requirements.
Analytical thinking – Ability to successfully assess a business' technical and operational needs.
Technical aptitude – As this role balances technology and business coordination, they are familiar with their organizations' technologies and processes every day.
Team coordination – Business analysts work closely with both development teams and business stakeholders, so they should have strong team leadership, collaboration, and coordination skills
Communication skills – The BA role requires excellent written and verbal communication to successfully prepare reports and interact with development team members and stakeholders.
A Gap Analysis on PMO Analyst and Business Analyst
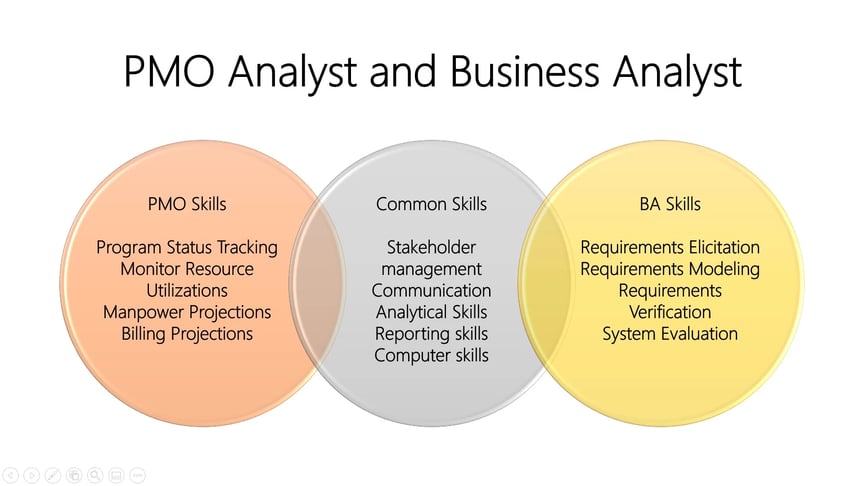 The above diagram indicates common skills available to PMO Analysts. It also shows additional skills needed to become an effective BA.
The above diagram indicates common skills available to PMO Analysts. It also shows additional skills needed to become an effective BA.
Steps to become Business Analyst From PMO Analyst
1. Learn the business analysis process.
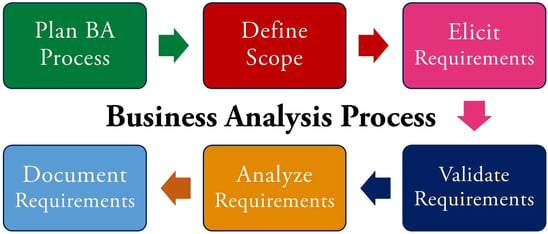
Like most other activities, business analysis also follows a process. Go ahead and read the Global Business Analysis Core Standard from IIBA (available to download for free). It is a short document of around 50 pages that gives a good idea of how business analysis is actually performed.
2. Learn the requirements modeling & management tools
Business analysts use several tools as part of their work. Learn how to use tools like MS Visio, Lucid chart, BizAgi Business process modeler, StarUML. Model, etc.
3. Get Involved in activities relating to Business Analysis

As the saying goes,' Practice makes a man perfect.' After learning about the basics of business analysis, it would be beneficial to involve yourself in projects by shadowing your organization's business analysis. This would allow you to practice the concepts you learnt.
4. Participate in Professional Groups, Webinars, and Conferences on Business Analysis
There are many professional special interest business analysis groups on LinkedIn and on forums on the web where one can discuss, participate, contribute, and learn the BA skills.
5. Get Business Analysis Certification
Getting a Business Analyst certification carries a lot of weight with organizations and will help you acquire the requisite knowledge. Certification can improve overall performance.
ECBA certification from IIBA is a good choice. ECBA not only gives a rock-solid foundation for getting into the BA profession but also helps with a globally recognized certification.
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

Business Analyst vs Data Analyst - similarities and differences

Should Business Analysts Learn Data Analytics - Adaptive US




No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think